Toenail fungal infections, also known as onychomycosis, can be caused by different types of fungi. The most common types of fungi responsible for toenail fungal infections are:
Dermatophytes: These are the most common culprits behind toenail fungal infections. The most prevalent dermatophyte species causing onychomycosis are Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton interdigitale.
Candida: This type of fungus, particularly Candida albicans, can also cause toenail fungal infections, though it is less common compared to dermatophytes.
Non-dermatophyte molds: Certain molds, such as Aspergillus species or Scopulariopsis brevicaulis, may also be responsible for toenail fungal infections in some cases.
It’s essential to identify the specific type of fungus causing the infection to determine the most appropriate treatment approach. A healthcare professional can conduct tests, such as microscopic examination or fungal cultures, to identify the causative fungus and recommend the appropriate treatment.
Over-the-counter antifungal medications: Topical creams, ointments, or sprays containing active ingredients like clotrimazole, terbinafine, or miconazole can be used to treat mild cases of toenail fungal infection.
Prescription antifungal medications: In more severe cases or when over-the-counter treatments are ineffective, a doctor may prescribe oral antifungal medications such as terbinafine, itraconazole, or fluconazole. These medications are taken for several weeks to months.
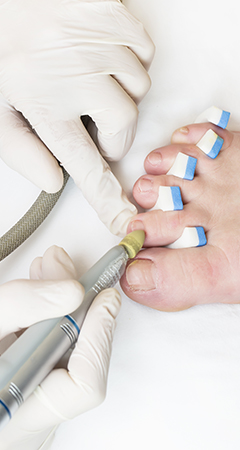
Nail debridement: Trimming and filing the affected nail can help reduce the infection’s severity and improve the effectiveness of topical treatments.
Nail lacquer: Prescription-strength antifungal nail lacquers containing ciclopirox or amorolfine are applied directly to the infected nail and surrounding skin.
Laser therapy: Some medical professionals use laser treatment to target and destroy the fungus in the toenail.
Avoidance of nail polish and artificial nails: These can trap moisture and worsen the infection.
Good foot hygiene: Keeping the feet clean and dry, using antifungal powders or sprays in shoes, and wearing breathable socks can help prevent further spread or reinfection.
Sterilizing nail care tools: Regularly disinfecting nail clippers and other tools used on the infected nail can prevent the spread of fungus to other nails.
It’s essential to follow the treatment plan consistently and consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and personalized recommendations.
